Rehabilitation is not just medical management; it’s about rejuvenating life. Rehabilitation has multiple subtypes depending upon their limitations and their goals, outcomes, and how they change lives.

Close your eyes and imagine this for a moment.
An IT professional in his 50s suffers a stroke. Just yesterday, he was doing his job, walking to the market, and living a full life. Today, he struggles to hold the mouse and press the key. Same stroke make a sales person unable to say a full sentence. Both family sits around hospital bed asking the one question, every family asks:
“Will he ever be the same again?”
This is where rehabilitation steps in. Quietly, patiently, and powerfully.
Rehabilitation is not about “curing” everything. It is about rediscovering ability, about crossing the bridge from survival to living. It helps people with health conditions, disabilities, or injuries find their way back to independence and dignity. Whether it is physiotherapy after a fracture, speech therapy for someone recovering from brain injuries, occupational therapy for hand function, or cardiac rehabilitation after surgery, each type of rehabilitation focuses on one simple goal: to improve quality of life.

Let’s explore the different types of rehabilitation, their objectives, outcomes, and why millions of people worldwide seeking rehabilitation at some point in their lives. If you’re looking for the right support, a Rehabilitation Center in Kolkata can help rebuild lives with care and therapy.
Guided by a Rehab Physician in Kolkata, recovery plans focus not just on treatment, but on restoring independence and daily living.
Misconceptions About Rehabilitation
Many people think of rehabilitation as being only for the severely disabled, or for those that are “stuck in bed.” The truth is that rehabilitation is for any person with health issues that is interfering with everyday life, even if that means walking up and down stairs, grasping a coffee cup, or walking to the mailbox.
Many people think of rehabilitation as physiotherapy. While it certainly can be that – and much more! Rehabilitation can affect things like speech and language, memory and cognition, returning to work, as well as mental and emotional health. For that comprehensive rehabilitation is needed, which need a team consists of occupational therapist, speech & language pathologist, psychologist, rehab nurse, social worker and obviously physiotherapist; led by Rehab Physician.
Rehabilitation is often thought to be a service for people who have fallen, been in a serious accident, or undergone surgery, but can also benefit people working to manage chronic health conditions that affect them every day, like heart disease, lung disease, or arthritis. For example, a PMR Doctor in Kolkata can help design a program tailored to these conditions.
Rehabilitation, the term often brings drug addiction in mind, but it’s small part of psychological rehabilitation.
There is the misconception that rehabilitation happens overnight, instantly. But it needs patience, and can only be achieved with the help of some extraordinary therapists, teamwork, and small successes along the way.
Rehabilitation at its core is about not only focusing on what you cannot do. It is about discovering what you can do; and supporting you in a journey back to living a life that is meaningful to you.
Comprehensive List of 10 Types of Rehabilitation
We’ll cover:
- Physical Rehabilitation
- Neurological Rehabilitation
- Amputation rehabilitation
- Paediatric rehabilitation
- Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation
- Geriatric Rehabilitation
- Cardiac & Pulmonary Rehabilitation
- Cancer rehabilitation and palliative care
- Addiction Rehabilitation
- Psychological Rehabilitation
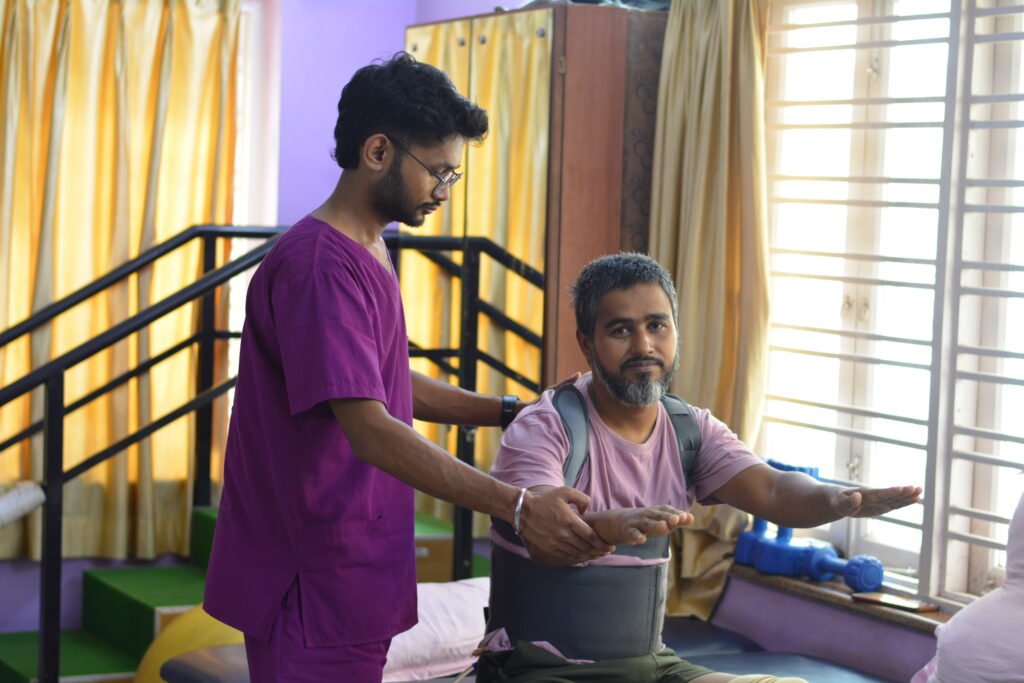

1. Physical Rehabilitation
Physical rehabilitation is about helping people regain strength, mobility, and independence after an injury, surgery, or health condition. Think of it as teaching the body to trust itself again.
Physical therapy (or physiotherapy) is one of the most common rehabilitation services. It helps patients recover after fractures, joint replacements, sports injuries, or surgeries. Physical therapists use strengthening exercises, stretches, balance training, and sometimes assistive technology to support recovery.
Objectives
● Improve strength, balance, and flexibility
● Reduce pain and stiffness
● Restore mobility for daily activities
● Prevent future injuries
Outcomes
● Patients return to walking independently
● Athletes recover to play their sport again
● Elderly regain balance, reducing fall risk
Common Cases
● Post-surgery (knee or hip replacement)
● Sports injuries (ACL tear, fractures)
● Stroke survivors regaining mobility Related Therapies
● Physiotherapy
● Occupational therapy for daily activities
Related Therapies
- Physiotherapy
- Occupational therapy for daily activities
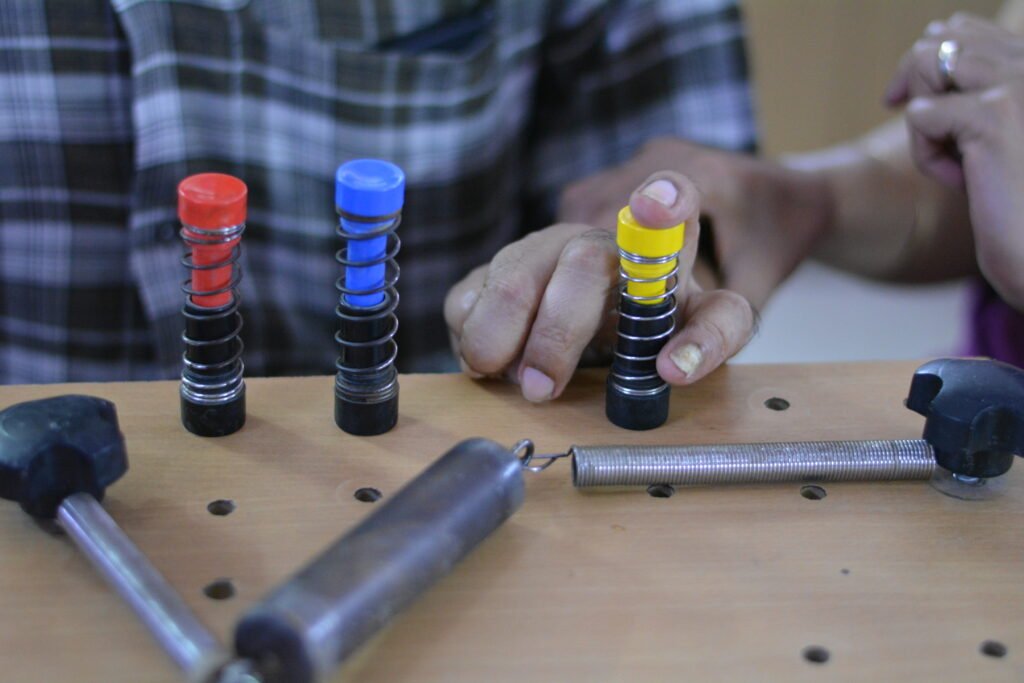

2. Neurological Rehabilitation
It is rehabilitation designed for individuals who have disorders of the brain, spinal cord or nerves. It can be as simple as teaching the nervous system to relearn and rebuild step by step.
Neurological rehabilitation is focused on illnesses or conditions such as stroke, spinal-cord injury, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and traumatic brain injuries, to name only a few.
Rehabilitation professionals could use a combination of physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, or cognitive rehabilitation according to Neurological deficit.
Objectives
● Restore motor skills and coordination
● Rebuild speech and communication
● Mange swallowing difficulty
● Manage spasticity, weakness, or tremors
● Boost memory and cognitive functions
Outcomes
● A stroke survivor speaks again after months of therapy
● A spinal cord injury patient learns to use a wheelchair confidently
● A Parkinson’s patient regains stability and reduces falls
Common Cases
● Stroke
● Spinal cord injuries
● Traumatic brain injuries
● Parkinson’s disease
Related Therapies
- Speech and language therapy
- Cognitive rehabilitation therapy
- Assistive technology
3. Amputation Rehabilitation
Amputation rehabilitation is about helping people who have lost their limb due to trauma or other medical issues, to return to work and society. It is not just about mobility but finding jobs about adapting skills, retraining, and supporting individuals to live independently with dignity. Rehabilitation professionals prescribe prosthetic limb after assessment and orthotics prepare it as per need. Then training with prosthesis take time to cope in.
Objectives
- · Increase muscle strength of residual muscles
- · Maintain range of motion of joints
- · Manage pain
- · Prepare for prosthesis
- · Prosthetic training
Outcomes
- · Independent mobility
- · workplace adaptation
- · Perform activity of daily living alone
4. Paediatric Rehabilitation
It deals children with disease like, cerebral palsy, club foot, muscular dystrophy etc. They need special attention in gait, balance, hand function and psychological development. Orthosis and modified shoe is often used for these programmes.
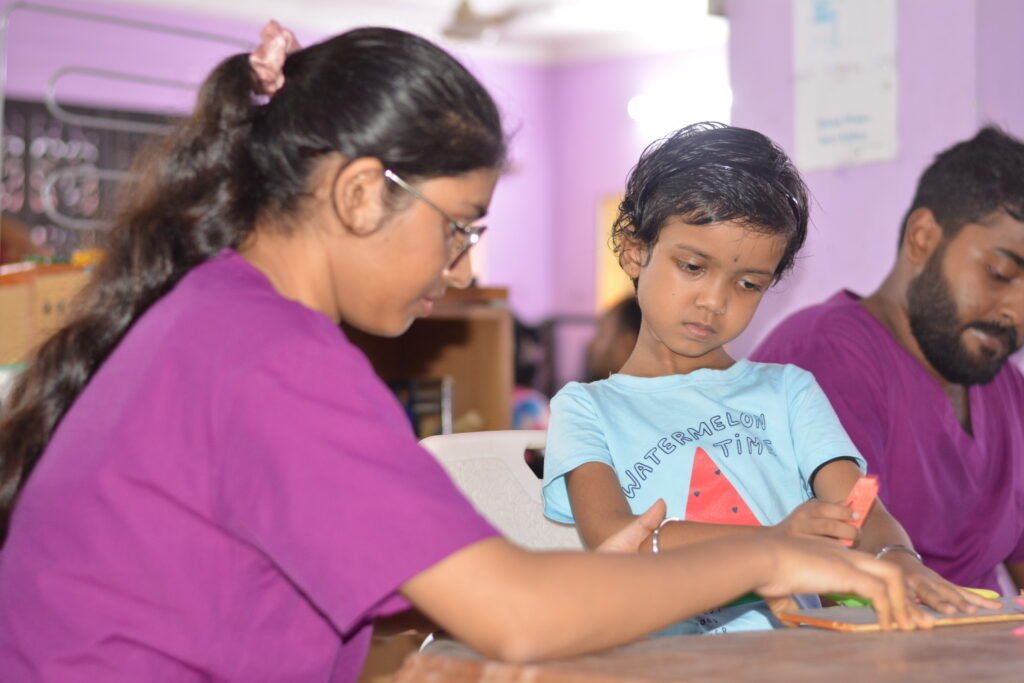

Objective
- Faster achievement of developmental milestones
- Gait pattern improvement
- Hand function training
- Balance training
- Orthotic support
- Shoe modification
- Rehab surgery
Outcome
- Achieve functional independence
- Unassisted mobility
- Incorporating into society
Common cases
- Cerebral palsy,
- club foot,
- Muscular dystrophy
5. Musculoskeletal & Orthopedic Rehabilitation
This form of rehabilitation helps people recover from bone, joint, and muscle conditions.
It includes therapy for fractures, arthritis, back pain, and orthopaedic surgeries including joint replacement, tendon transfer, and capsular release.
Orthopedic rehabilitation involves physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and sometimes assistive devices.
Studies show that physical therapy reduces pain and improves mobility in up to 80% of patients with musculoskeletal disorders such as arthritis or back pain.
Objectives
- Restore movement after injuries
- Reduce chronic pain
- Help patients return to daily activities
Outcomes
- Pain-free walking
- Faster healing after surgery
- Return to sports or work
Common Cases
- Hip and knee replacement
- Arthritis
- Spinal injuries
Related Therapies
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
6. Geriatric Rehabilitation
Geriatric rehabilitation focuses on complete recovery from age related illness, or chronic disease.
It is comprehensive rehabilitation involving doctors, nurses, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists, psychologist and rehab nurse. Rehabilitation starts with individualised customized programs.
According to the World Health Organization, an estimated 2.4 billion people globally are currently living with a health condition that could benefit from rehabilitation
Objectives
- Support elderly patients post illness
- Prevent complications
- Improve daily functioning Outcomes
- Patients recover faster after illness.
- Reduced hospital readmission
- Improved overall quality of life
Common Cases
- Post-surgical patients Related Therapies
- Deconditioning
- Osteoporotic fracture
- Kyphoscoliosis
7. Cardiac & Pulmonary Rehabilitation
It is rehabilitation designed for heart and lung pathology. It art of comeback from deconditioning of heart and lungs .
Cardiac rehab supports recovery after heart attacks, surgeries, or heart failure. Pulmonary rehab helps patients with COPD, asthma, or lung surgery recover.
Objectives
- Strengthen heart and lungs
- Teach safe exercises and breathing techniques
- Reduce risk of complications
Outcomes
- Improved stamina
- Lower hospital readmissions
- Increased confidence in daily activities
Common Cases
- Patients after heart surgery
- COPD patients
- Asthma management
Related Therapies
- Respiratory therapy
- Counseling for lifestyle changes
8. Cancer rehabilitation & Palliative care
This is about reintegrating individuals back into their life with cancer related disability. Community programs aim to reduce isolation and promote inclusion.
Objectives
- Rebuild confidence
- Promote participation in society
- Reduce stigma Outcomes
- Better mental and emotional health
- Reduce cancer pain.
Outcome
- Pain free life
- Add quality in life
- Functional independence
9. Addiction Rehabilitation
Addiction rehabilitation is designed to help people recover from drug, alcohol, or behavioral addictions. It is about rebuilding control over one’s life.
Addiction rehab combines behavioral therapy, counseling, group support, and medical interventions. The goal is not only detoxification but also long-term recovery.
Objectives
- Help patients overcome dependence
- Teach coping skills
- Rebuild relationships and trust
- Prevent relapses
Outcomes
- Individuals live addiction-free lives
- Families are reunited
- Improved mental and physical health
Common Cases
- Alcohol rehabilitation
- Drug rehabilitation
- Behavioral addictions (gaming, gambling)
Related Therapies
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Group therapy
- Psychological rehabilitation
10. Psychological Rehabilitation
It is rehabilitation for the mind and emotions, especially after trauma, mental health disorders, or psychological injury.
This type focuses on anxiety, depression, PTSD, or trauma recovery. Therapy aims to improve coping skills, emotional strength, and social reintegration.
Objectives
- Support mental health recovery
- Reduce symptoms of trauma or depression
- Improve interaction with environment
- Restore self-confidence
Outcomes
- A patient with PTSD reintegrates into society
- Depression patients regain normal routines
- Families cope better with mental health disorders
Common Cases
- Trauma survivors
- Patients with depression or anxiety
- People with severe stress
Related Therapies
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Group therapy
- Music or art therapy
Conclusion
Rehabilitation is more than just get back your life, it’s returning to recovery and about rediscovering life.
From physical therapy following surgery to neurological rehabilitation with stroke clients, addiction recovery, and cardiac rehabilitation- there is a single purpose to every rehabilitation type to restore people’s independence, dignity, and hope. As the World Health Organization says, rehabilitation is part of universal health coverage. Every person, at some point in life, may need rehabilitation.
If you or your loved one may benefit from rehabilitation services, remember this: progress is possible, no matter how small the step.
Take the First Step Towards Recovery Today!
Don’t wait for tomorrow. If you or your loved one may need rehabilitation, start today.